DeFi’s promise of decentralized cash, as we now have painfully seen, comes with the peril of irreversible code vulnerabilities, poor structure, and insufficient auditing. So it’s not simply as a magnet for traders and builders but additionally for stylish cybercriminals.
Since Bitcoin’s inception, the crypto house has seen a protracted line of hacks, from easy phishing scams to extremely subtle good contract exploits. In keeping with Chainalysis, DeFi protocol hacks had been a significant driver behind the surge in stolen cryptocurrency throughout 2021 and 2022, with cybercriminals stealing over $3.1 billion in DeFi-related breaches in 2022 alone.
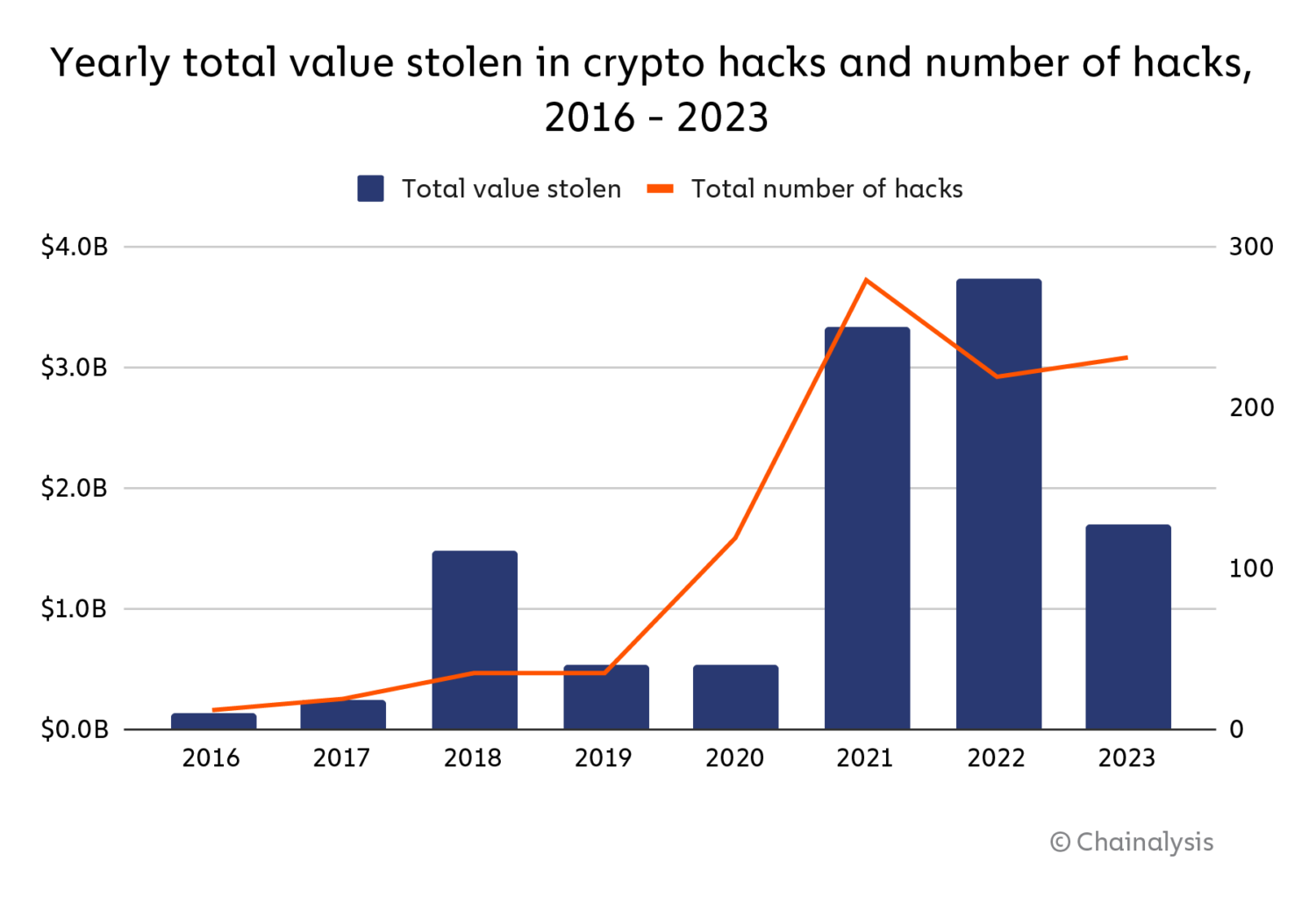
The unhappy however true truth is that attackers are rising extra refined as infrastructure scales. The quantity of hacking incidents jumped from 282 in 2023 to 303 in 2024, highlighting how susceptible these techniques stay. The largest heists typically stem from a single flaw—whether or not it’s an missed vulnerability in good contract code, a compromised non-public key, or the exploitation of centralized management inside a supposedly decentralized system.
This text seems at a few of the most infamous breaches in crypto and DeFi historical past, breaking down what went improper, how the trade responded, and what builders and traders can be taught going ahead.
The Most Devastating DeFi Exploits to Date
1. Mt. Gox (2014)
Loss: 850,000 BTC ($460 million on the time)
Sort of Assault: Change Sizzling Pockets Exploit
Vulnerability: Transaction malleability + lack of inner controls
Restoration: Partial, about 200,000 BTC was recovered
Mt. Gox wasn’t a DeFi protocol within the trendy sense, however the scale of the breach revealed in 2014 makes it a foundational occasion in crypto’s safety narrative. At its peak, Mt. Gox dealt with over 70% of all international Bitcoin transactions.
However behind the scenes, its safety practices had been dangerously flawed. The change relied closely on scorching wallets, lacked primary inner audits, and didn’t reconcile balances towards blockchain information—leaving the door huge open for theft that most likely went on for greater than half of existence in full operation.
One major vulnerability the attackers exploited was a bug often known as transaction malleability, which allowed attackers to change transaction IDs earlier than affirmation. This tricked Mt. Gox into considering withdrawals had failed, prompting it to resend funds—time and again.
In early 2014, withdrawal delays sparked person panic. On February 7, Mt. Gox froze all Bitcoin withdrawals, citing “technical points.” Lower than a month later, it declared chapter. And a deeper inner investigation revealed the horrifying fact—850,000 BTC had vanished. This revelation despatched shockwaves by the crypto trade, inflicting widespread panic.
A small glimmer of hope emerged in March 2014, when the change introduced it had situated 200,000 BTC in an old-format pockets. This decreased the full losses to 650,000 BTC, nevertheless it was nonetheless an astronomical quantity.
2. Poly Community (2021) – The Largest DeFi Hack… Briefly
Loss: Over $610 million
Sort of Assault: Sensible Contract Exploit
Vulnerability: Cross-chain verification flaw
Restoration: Most funds had been returned by the attacker
In August 2021, the Poly Community, a protocol enabling cross-chain asset swaps, was drained of $610 million price of a number of cryptocurrencies. The attacker exploited a vulnerability within the contract calls that Poly Community used for its cross-chain transactions. This flaw allowed the hacker to bypass the safety checks and authorise unauthorised withdrawals of funds from the platform.
The Poly Community group was in a position to rapidly establish the pockets addresses utilized by the attacker to empty the funds throughout the completely different blockchains. As quickly as this was found, the neighborhood, together with exchanges, started blacklisting the pockets addresses to forestall additional motion of the stolen property.
In an uncommon twist, the hacker returned a lot of the funds after claiming the exploit was a white-hat train. Whereas the injury was reversed, the occasion uncovered the complexities of cross-chain structure and the necessity for hermetic validation mechanisms.
3. Wormhole (2022) – $320M Drained from a Bridge
Loss: ~120,000 ETH (then ~$320 million)
Sort of Assault: Sensible Contract Exploit
Vulnerability: Signature verification bypass
Restoration: Losses had been coated by Leap Crypto, standing of misplaced crypto is unknown
Wormhole was one of many earliest Solana-Ethereum bridges facilitating cross-chain token transfers. In February 2022, an attacker discovered a bug within the verification logic and minted 120,000 Wrapped Ether (wETH), price over $320 million on the time, with out offering actual ETH on Ethereum. The attacker bypassed Wormhole bridge’s safety mechanism on the Solana blockchain and injected pretend information into the system. This information spoofed the signature validation course of, tricking the system into considering that the transaction was reliable. As soon as the attacker had efficiently minted the tokens, they moved them to Ethereum and laundered the stolen funds.
After the breach, the Wormhole group rapidly patched the vulnerability to keep up belief within the protocol, and Leap Buying and selling, an investor in Wormhole, coated the loss. Nonetheless, the hack underscored the fragility of bridge protocols, now considered one in all DeFi’s most susceptible vectors.
4. Ronin Bridge (2022)
Loss: ~$625 million
Sort of Assault: Personal key compromise
Vulnerability: Centralized validator mannequin
Restoration: Partial; some property recovered; ongoing lawsuits and investigations
The Ronin Bridge was utilized by Sky Mavis, the creator of in style P2E sport, Axie Infinity, to maneuver property between Ethereum and the Ronin Community. In March 2022, attackers stole roughly 173,600 ETH and 25.5 million USDC, totaling round $625 million. The breach went unnoticed for practically every week till a failed withdrawal raised pink flags.
The vulnerability stemmed from a brief association months earlier, when the sport’s governance board, AxieDAO, gave Sky Mavis permission to signal transactions on its behalf. Critically, this allowlist was by no means revoked. The attacker exploited the oversight, having access to 4 Sky Mavis validators and one DAO-controlled validator—simply sufficient to pretend authorization for 2 large withdrawals.
Whereas Sky Mavis has since expanded its validator set and launched stronger monitoring, the hack reignited debate over how centralized some supposedly “decentralized” techniques actually are.
5. Bybit (2025)
Loss: ~$1.5 billion
Sort of Assault: Entrance-end hijack
Vulnerability: Developer atmosphere compromised, malicious JavaScript injected into pockets interface
Restoration: Underneath investigation; funds largely unrecovered
In February 2025, Bybit turned the sufferer of the biggest crypto heist to this point—not by a wise contract flaw, however a compromised person interface. The attackers infiltrated the event atmosphere of Protected, a pockets infrastructure supplier, and embedded malicious JavaScript into its UI library.
This rogue script altered what customers noticed when authorizing transactions. Hundreds, together with Bybit, unknowingly signed permissions that redirected funds to attacker-controlled wallets. The exploit allowed over 401,000 ETH to be drained from Bybit’s chilly pockets in a single malicious transaction disguised as routine.
Though the back-end contracts and blockchain techniques remained untouched, the assault confirmed that even probably the most safe protocols are susceptible when front-end techniques are compromised. The incident sparked pressing calls throughout the trade to deal with UI code with the identical rigour as good contracts—highlighting a blind spot in crypto safety structure.
Classes Discovered
Every hack/assault described above presents a unique lesson for DeFi groups, safety auditors, and customers.
1. Use Chilly Wallets + Multisig for Asset Storage
Mt. Gox taught the trade the risks of scorching wallets. Most exchanges immediately safe property in chilly storage, with multisig techniques guaranteeing no single level of failure. In case your DeFi protocol holds important property, implement multisig and chilly pockets separation.
Then again, customers ought to keep away from storing giant quantities of cryptocurrency on centralized exchanges. Not your keys, not your wallets, not your funds. The collapse of Mt. Gox left 1000’s of customers with out entry to their funds. Self-custody options, corresponding to {hardware} wallets, supply better safety.
2. Audit Sensible Contracts Usually
Poly Community and Wormhole had been each victims of coding flaws that might have been recognized upfront. Audits are actually frequent—however they’re not bulletproof. Groups should run a number of impartial audits, interact in bug bounty packages, and revisit contracts because the protocol evolves.
3. Bridge Protocols Are Nonetheless a Minefield
Each Wormhole and Ronin spotlight the systemic danger in bridge structure. Bridges depend on off-chain verification, which makes them essentially extra fragile than on-chain swaps. Builders ought to decrease the assault floor and discover trustless options like zero-knowledge proofs and native asset bridges.
4. Entrance-Finish Safety Issues
Bybit’s case makes one factor clear: even a well-secured blockchain is susceptible if the interface is compromised. All internet interfaces have to be remoted, monitored, and topic to inner code audits. Consumer-signed transactions want readability and safety warnings to forestall deception.
5. Decentralization Should Be Actual, Not Simply Claimed
Ronin was exploited as a result of validator centralization—solely 5 of 9 validators wanted to log off on transactions. To name a community decentralized, it have to be functionally and technically distributed. Something much less is a advertising and marketing gimmick with safety implications.
6. Bug Bounties Are Cheaper Than Exploits
Within the case of Poly Community, a hacker returned $610 million, doubtlessly avoiding a everlasting loss. A strong bug bounty program presents white hats incentives to report points slightly than exploit them. In the event you don’t pay hackers to seek out your bugs, you could find yourself paying them much more afterwards.
READ MORE: Methods to Deal with Crypto Hacks for a Safer Blockchain Future
Remaining Thought: Belief is Constructed on Code—and Tradition
Crucial takeaway from these DeFi hacks isn’t that good contracts are harmful—it’s that decentralized techniques require an hermetic structure, clear tradition, and fixed vigilance. Not like banks, DeFi protocols can’t reverse fraudulent transactions or pause the system. As soon as an exploit is triggered, the funds are sometimes gone for good.
Nonetheless, these incidents have pushed innovation. The house has matured: multisig wallets are normal, audits are anticipated, and front-end safety is below better scrutiny. Every hack has served as an costly lesson, forcing tasks to lift their requirements and customers to change into extra security-conscious.
As DeFi continues to evolve, the trade should keep in mind that the purpose isn’t simply constructing protocols that work—it’s constructing protocols that may’t be damaged.
Disclaimer: This text is meant solely for informational functions and shouldn’t be thought of buying and selling or funding recommendation. Nothing herein needs to be construed as monetary, authorized, or tax recommendation. Buying and selling or investing in cryptocurrencies carries a substantial danger of monetary loss. At all times conduct due diligence.
If you wish to learn extra market analyses like this one, go to DeFi Planet and observe us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Fb, Instagram, and CoinMarketCap Group.
Take management of your crypto portfolio with MARKETS PRO, DeFi Planet’s suite of analytics instruments.”
The put up The Greatest Hacks and Exploits in DeFi Historical past & What We Can Be taught from Them appeared first on DeFi Planet.


